Chapter 4: Use Container to run Nginx and Docker commands
1. Use docker to run Nginx
1.1 Use 'docker run' to run Nginx
1.1.1 Inpect the process of downloading the image
Loking for the image locally
# docker run -d nginx:latest
Unable to find image 'nginx:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/nginx
a2abf6c4d29d: Downloading 1.966MB/31.36MB
a9edb18cadd1: Downloading 1.572MB/25.35MB
589b7251471a: Download complete
186b1aaa4aa6: Download complete
b4df32aa5a72: Waiting
a0bcbecc962e: Waiting
1.1.2 Check the running status of containers
# docker run -d nginx:latest
9834c8c18a7c7c89ab0ea4119d11bafe9c18313c8006bc02ce57ff54d9a1cc0c
# Command explanation
docker run (start a container based on a image)
-d (execute the commands in the image by daemon way)
nginx (the name of the image)
latest (tag/version of the image)
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9834c8c18a7c nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint.…" 24 seconds ago Up 23 seconds 80/tcp condescending_pare
docker ps is like 'ps' in linux, used to check all running containers
docker ps outputs
| CONTAINERID | IMAGE | COMMAND | CREATED | STATUS | PORTS | NAMES |
| 9834c8c18a7c | nginx:latest | "/docker-entrypoint.…" | 24 seconds ago | Up 23 seconds | 80/tcp | condescending_pare |
1.2 Access to the service running in the container
1.2.1 Get container's ip address
Don't have to do this in production
# docker inspect 9834
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2", 容器IP地址
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "d3de2fdbc30ee36a55c1431ef3ae4578392e552009f00b2019b4720735fe5a60",
"EndpointID": "d91f47c9f756ff22dc599a207164f2e9366bd0c530882ce0f08ae2278fb3d50c",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2", (here)
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
}
]
#Explaination:
docker inspect is used to check containers information
9834 is the first 4 digits of the container id, we can use a short id sequence to find a container, don't have to copy the whole id
1.2.2 Network in container
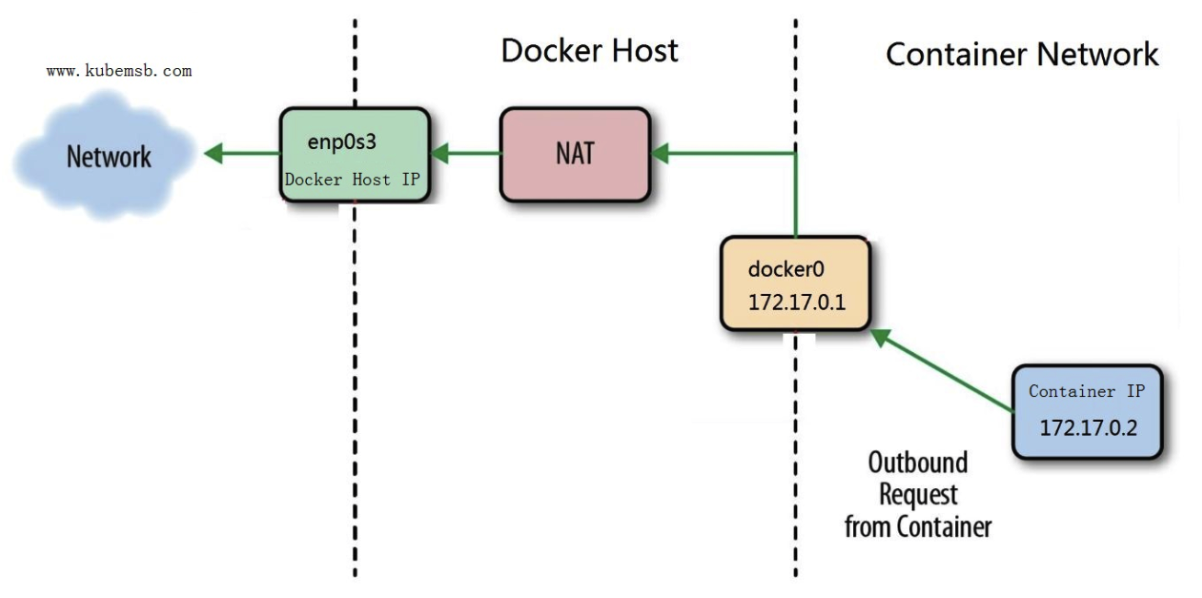
# ip a s
......
docker0 is the default bridge network that Docker creates when it is installed. It is a virtual bridge that allows Docker containers to communicate with each other and with the host system, as well as providing connectivity to external networks through the host's network interface. By default, all Docker containers are attached to the docker0 bridge unless otherwise specified. The IP address range for docker0 is 172.17.0.0/16.
5: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:d5:c3:d4:cc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::42:d5ff:fec3:d4cc/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
# It is used to connect the network of a container to the host system, and is located in the same namespace as the virtual networking devices within the container.
9: veth393dece@if8: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP group default
link/ether 02:e3:11:58:54:0f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet6 fe80::e3:11ff:fe58:540f/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
1.2.3 Use curl to access
# curl http://172.17.0.2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
2. Docker commands
2.1 Get help with docker commands
# docker -h
Flag shorthand -h has been deprecated, please use --help
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides
DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal")
(default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
app* Docker App (Docker Inc., v0.9.1-beta3)
builder Manage builds
buildx* Docker Buildx (Docker Inc., v0.7.1-docker)
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
image Manage images
manifest Manage Docker image manifests and manifest lists
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
scan* Docker Scan (Docker Inc., v0.12.0)
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
2.2 Official docs on commands
2.3 Docker commands usage
2.3.1 docker run
# docker run -i -t --name c1 centos:latest bash
[root@948f234e22a1 /]#
docker run: When running a command in a container, the command is the main process. If there is no command, the container will exit immediately.
-i: interactive
-t: terminal
--name: name the container to c1
centos:latest: use the latest centos image
bash: execute bash command in container
this is the host name:
[root@948f234e22a1 /]#
check network info in container
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# ip a s
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
12: eth0@if13: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:03 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.3/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
check processes in container
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# ps aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.1 12036 2172 pts/0 Ss 09:58 0:00 bash
root 16 0.0 0.0 44652 1784 pts/0 R+ 10:02 0:00 ps aux
check user info in the container:
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:65534:65534:Kernel Overflow User:/:/sbin/nologin
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
systemd-coredump:x:999:997:systemd Core Dumper:/:/sbin/nologin
systemd-resolve:x:193:193:systemd Resolver:/:/sbin/nologin
check directory:
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# pwd
/
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# ls
bin etc lib lost+found mnt proc run srv tmp var
dev home lib64 media opt root sbin sys usr
exit the container:
[root@948f234e22a1 /]# exit
exit
[root@localhost ~]#
2.3.2 docker ps
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
948f234e22a1 centos:latest "bash" 10 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago c1
| CONTAINERID | IMAGE | COMMAND | CREATED | STATUS | PORTS | NAMES |
| 948f234e22a1 | centos:latest | "bash" | 10 minutes ago | Exited (0) 2 minutes ago | c1 |
docker ps -a: check all containers including running and stopped
2.3.3 docker inspect
# docker run -it --name c2 centos:latest bash
[root@9f2eea16da4c /]#
note:
use ctrl p+q can exit without terminate the container.
# docker inspect c2
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "d3de2fdbc30ee36a55c1431ef3ae4578392e552009f00b2019b4720735fe5a60",
"EndpointID": "d1a2b7609f2f73a6cac67229a4395eef293f695c0ac4fd6c9c9e6913c9c85c1c",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
}
]
2.3.4 docker exec
# docker exec -it c2 ls /root
anaconda-ks.cfg anaconda-post.log original-ks.cfg
docker exec: execute a command outside the container
-it: interactive terminal
2.3.5 docker attach
[root@localhost ~]# docker attach c2
[root@9f2eea16da4c /]#
docker attach is like ssh, allow us to enter in to the container
When using `docker attach` to exit a container, if you do not need the container to continue running, you can simply use the `exit` command to terminate the container. However, if you want to keep the container running in the background, you can detach from it without stopping it by pressing `Ctrl + P` followed by `Ctrl + Q`. This will return you to the host shell without terminating the container.
2.3.6 docker stop
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9f2eea16da4c centos:latest "bash" 22 minutes ago Up 22 minutes c2
# docker stop 9f2eea
9f2eea
# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9f2eea16da4c centos:latest "bash" 22 minutes ago Exited (137) 4 seconds ago c2
2.3.7 docker start
# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9f2eea16da4c centos:latest "bash" 22 minutes ago Exited (137) 4 seconds ago c2
# docker start 9f2eea
9f2eea
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9f2eea16da4c centos:latest "bash" 24 minutes ago Up 16 seconds c2
2.3.8 docker top
in Docker Host, check processes in the container
# docker top c2
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 69040 69020 0 18:37 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
| UID | PID | PPID | C | STIME | TTY | TIME | CMD |
| root | 69040 | 69020 | 0 | 18:37 | pts/0 | 00:00:00 | bash |
The docker top command is used to view information about the processes running in a container from the Docker host's perspective. It allows you to see the list of processes that are running inside the container along with their process IDs (PIDs), and resource utilization statistics such as CPU and memory usage.
On the other hand, docker exec -it c2 ps -ef command is used to run the ps -ef command inside the container with ID or name c2. This command allows you to view the processes running inside the container from within the container itself, rather than from the Docker host's perspective.
Outputs explanation:
UID: user id in container
PID: process id in container
PPID: parent process id
C: CPU
STIME: start time
TTY: terminal
TIME: running time
CMD: executed command
2.3.9 docker rm
If the container is stopped, use this command to delete it directly; if the container is running, you need to shut down the container in advance before deleting the container. The following demonstrates the method of deleting after the container is running and shutting down.
2.3.9.1 Specify the container ot be removed
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9f2eea16da4c centos:latest "bash" 2 days ago Up 3 seconds c2
# docker stop c2
or
# docker stop 9f2eea16da4c
# docker rm c2
or
# docker rm 9f2eea16da4c
2.3.9.2 batch deletion
# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
948f234e22a1 centos:latest "bash" 2 days ago Exited (0) 2 days ago c1
01cb3e01273c centos:latest "bash" 2 days ago Exited (0) 2 days ago systemimage1
46d950fdfb33 nginx:latest "/docker-ent..." 2 days ago Exited (0) 2 days ago upbeat_goldberg
# docker ps --a | awk '{if (NR>=2){print $1}}' | xargs docker rm
